Retrieve public key for the FE's JWT response (1.0)
Whenever you call a function via the JS function, you will get a JWT to ensure the payload is actually from PayPay. We will walk you through the steps in how to verify the JWT, how to reduce the necessary calls to Open Payment API service, and what fields you should be checking to ensure it's a payload from PayPay.
To start utilizing our Open Payment API platform, at first the business needs to be onboarded as a PayPay merchant.
This process usually consists of information collection, manual verification, contract confirmation and credentials issuance.
After becoming a merchant on PayPay, the following items would be setup for the client:
- api key and secret
- webhook endpoints
- client IP whitelist
- merchant identifier (merchant_id) (for agent client)
This setup can be managed using our merchant panel/ getting in touch with the sales representative.
Everything related to OPA API Authorization is described here.
PayPay OPA uses HTTP response status codes and OPA error codes to indicate the success or failure of requests. With this information, you can decide what error handling strategy to use. In general, PayPay OPA returns the following HTTP response status codes.
Common response code
| Status | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | SUCCESS | Success |
| 400 | KID_NOT_FOUND | The KID was not found in the system. |
| 401 | UNAUTHORIZED | This status code indicates an authorization error, like no valid api key and secret provided. |
| 429 | RATE_LIMIT | This status code indicates that the client sent too many requests in a specific period of time, and hit the rate limits. You should slow down the request sending or contact us to raise your limit. |
| 500 | INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR | This status code indicates that something went wrong in PayPay side. |
| 503 | MAINTENANCE_MODE | Sorry, we are down for scheduled maintenance. |
| 503 | SERVICE_UNDER_MAINTENANCE | Sorry, we are down for scheduled maintenance. |
In principle, all API responses include an X-REQUEST-ID in the response header (with some exceptions).
When contacting PayPay support, please provide this request ID.
Format: Alphanumeric characters and hyphens (maximum 64 characters)
Example:
OPA45F681001AEF4605B2A50939F611F4B8
Each response from the frontend will be encrypted using a random pair of public/private key retrieved by our server. Inside the JWT's, you'll get a payload that contains the response from the backend. In order to decrypt the JWT token, we will provide you an api that gives you the public key given a KID. The KID can be retrieved inside the returned JWT.
After getting the KID, call the public key api that's explained further in this documentation to get the public key for KID.
Once you have the public key, please cache the KID with this public key to avoid always having to calling the get public key API every time.
NOTE: These pairs are ALWAYS renewed weekly on Tuesdays at 15:00 JST. Thus every Tuesday at 15:00, please empty the cache.
Get public key flow
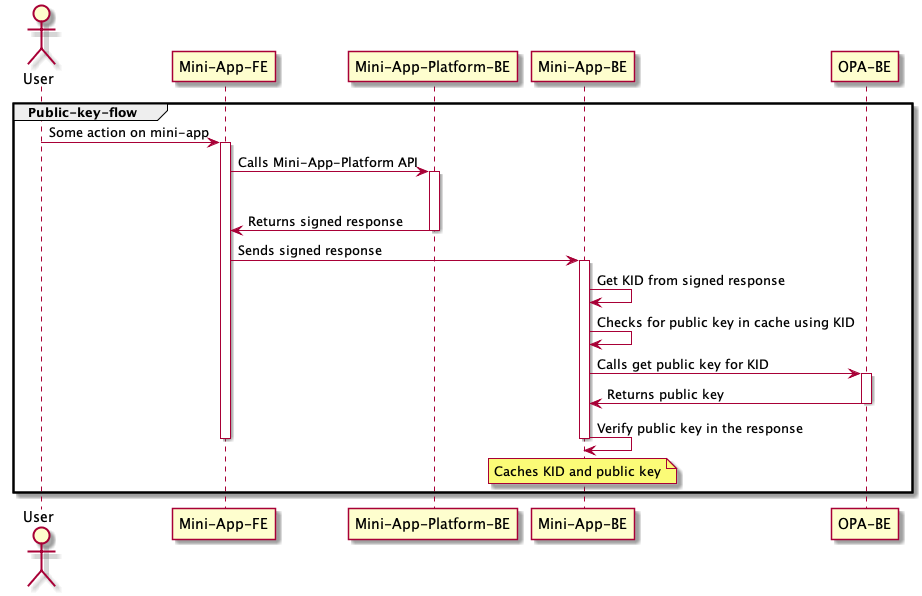
To verify the JWT received from server, you must first get the KID from the jwt token. For example, in Java you can get the KID by:
final DecodedJWT decodedJWT = JWT.decode(payload);
final String kid = decodedJWT.getKeyId();
Next, after getting the KID, call the publicKey api if and only if there's no cache value for it.
// setup...
final CacheServiceImplementation cacheServiceImplementation;
// ...
// inside some get public key method
String publicKey;
// we only call v1/publicKey if we don't know the public key.
if (cacheServiceImplementation.contains(KID)) {
// do not call publicKey api and instead retrieve it from the cache
publicKey = cacheServiceImplementation.get(KID)
}
else {
// call the publicKeyApi since we don't have the KID that contains a public key value
// curl example:
// curl "http://stg-api.paypay.ne.jp/v1/publicKey?kid=0b08710e-e8d6-4c4d-b46f-27509012ac21" \
// -H "Authorization: hmac OPA-Auth:a_1obUXXXXX_XXXX:BY8NnUuXXXXX_XXXXae8OXXXXX_XXXXP5Hhlx8+b0=:98aa04:1588839957:empty"
publicKey = Optional.ofNullable(restTemplate.exchange(
"http://stg-api.paypay.ne.jp/v1/publicKey/opa/api/v1/publicKey?kid={kid}", HttpMethod.GET,
new HttpEntity<>(headers),OPAPublicKey.class,kid,
)).map(OPAPublicKey::getData).map(OPAData::getPublicKey).orElseThrow(NoPublicKeyException::new);
// save the KID associated with the public and expire it next Tuesday at 15:00.
cacheServiceImplementation.put(KID, public)
}
Note: the above curl is just an example with masked fields. You must generate the hmac with your api key and secret.
When calling the api, you will get a response like the one in the bottom:
{
"resultInfo": {
"code": "SUCCESS",
"message": "Success",
"codeId": "08100001"
},
"data": {
"publicKey": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAi47XWBtFBi944WwTwkTm/yJeYqSXhKxnPMVa0M+PW7FbTqGQ2deeHAx9lC5MxkdnJfRPeOI+Zy7l9tJAN510gBin7QGH879B/5lxu887DuaN8ERn8T9g/2DXAzPq2roWCHtBkcfuHJtqBybVsBGZDrC54JutBDOl6ACnUYJbCIag6UBCwRkIxkA/9yRDGS6+uJkhpqPWFQdfwd8+8JP9D5c+dDEN9pwL6/X2kZkFKOdyheOiNrqjShokaNDYqu3vZbI40HI2b7SgTsF4elsyv5TBBjjTc9NfsLHELKEseCA9djDHNZksKHwU+fgXwY2bp+N/UdVW+BLqKNUDjkZGyQIDAQAB-----END PUBLIC KEY-----"
}
}
Before we look in how to verify the payload, let's look at the structure of the JWT:
{
"iss": "",
"exp": 1589531351,
"aud": "a_XXXXXXX",
"iat": 1589530451,
"payload": "{}"
}
In the audience, it will be your clientId.
The exp is when the JWT will expire.
The payload is where we will keep the response body.
Now let's verify the payload. First, let's make sure it's actually a valid public key. To do so, do the following:
final String yourPayload = ...
final String publicKey = "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAi47XWBtFBi944WwTwkTm/yJeYqSXhKxnPMVa0M+PW7FbTqGQ2deeHAx9lC5MxkdnJfRPeOI+Zy7l9tJAN510gBin7QGH879B/5lxu887DuaN8ERn8T9g/2DXAzPq2roWCHtBkcfuHJtqBybVsBGZDrC54JutBDOl6ACnUYJbCIag6UBCwRkIxkA/9yRDGS6+uJkhpqPWFQdfwd8+8JP9D5c+dDEN9pwL6/X2kZkFKOdyheOiNrqjShokaNDYqu3vZbI40HI2b7SgTsF4elsyv5TBBjjTc9NfsLHELKEseCA9djDHNZksKHwU+fgXwY2bp+N/UdVW+BLqKNUDjkZGyQIDAQAB-----END PUBLIC KEY-----";
final String key = publicKey.substring("-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----".length(), publicKey.indexOf("-----END PUBLIC KEY-----"));
byte[] decodedPublicKey = Base64.getDecoder().decode(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
X509EncodedKeySpec spec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(decodedPublicKey);
RSAPublicKey publicKey1 = (RSAPublicKey) KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA").generatePublic(spec);
Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.RSA256(publicKey1, null);
String payload;
try {
// verify with the payload.
DecodedJWT decodedJWT = JWT.require(algorithm).build().verify(yourPayload);
String audClientId = decodedJWT.getClaims().get("aud")
if (!audClientId.equals("MY_CLIENT_ID")) {
throw new MismatchClientIdException();
}
payload = decodedJWT.getClaims().get("payload");
} catch (Exception e) {
// handle invalid signature or any other error.
}
Once you get your payload, you should convert it to an object or map and should check the key "responseValidTill" inside the data field(e.g. payloadMap.get("data").get("responseValidTill")). If the responseValidTill(a long expressed in epoch time) is earlier than the time the response was received, the payload is invalid.
NOTE: the JWT will always expire in 15 minutes after creation.
After retrieving the public key, save the associated KID with this public key to not always call to OPA. You will need to call this weekly since the KIDs will be newly created on Tuesdays at 15:00.
Retrieves a public given a KID
When you retrieve the KID from the signed response returned from the FE's JWT, you will then call this api to get the public key.
query Parameters
| kid required | string The kid that's inside your signed response. |
Responses
Response samples
- 200
- 400
- 401
- 404
- 500
{- "resultInfo": {
- "code": "string",
- "message": "string",
- "codeId": "string"
}, - "data": {
- "publicKey": "string"
}
}